Nick
In Remembrance
HOW-TO
How to Enable the New Windows 10 Sandbox Feature to Safely Test Apps
ByBrian Burgess
Last Updated on December 21, 2018

Windows Sandbox in Windows 10 allows you to safely run untrusted apps in an isolated virtual environment and keep your main system safe from malware.
COMMENTS
When Microsoft rolled out Windows 10 build 18305 to Insiders in the Fast ring, it also madeWindows Sandbox available. The sandbox feature allows you to run sketchy or untrusted applications in an isolated environment that doesn’t affect the rest of your system. Typically, you could do this by setting up a virtual machine – which takes time and system resources. But Microsoft is making the process easier by implementing Windows Sandbox in the upcoming feature update. Here is a look at how to enable and use the new feature.
Note: This is only available for Pro and Enterprise versions of Windows 10 (build 18305 or higher). Your system will also need to meet the following requirements:
To enable Windows Sandbox, hit the Windows key and type: turn windows features on or off and choose the top result or hit Enter.
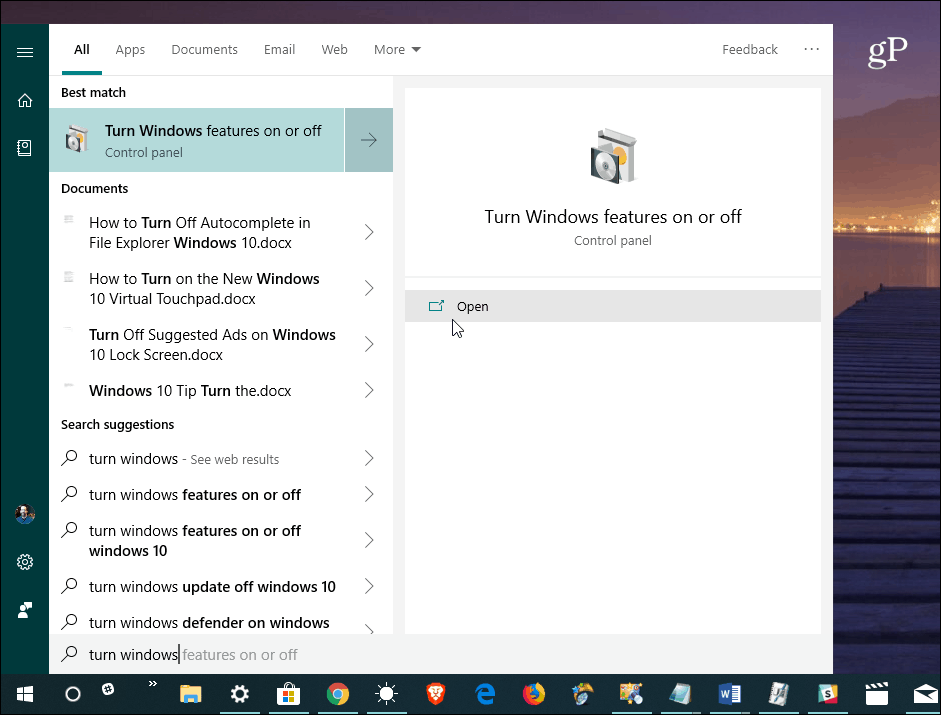
The Windows Features window where you can turn different features on or off will open. Scroll down the list and check the “Windows Sandbox” option and click OK. Then simply follow the on-screen wizard to finish installing it – a restart will be required.
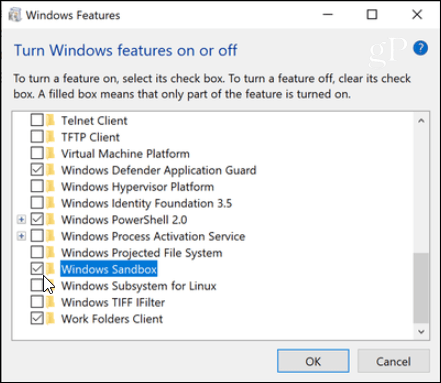
Once installed, you can simply run Windows Sandbox from the Start menu with elevated privileges. Copy the executable file you want to run to the Windows Sandbox and run it like you normally would.
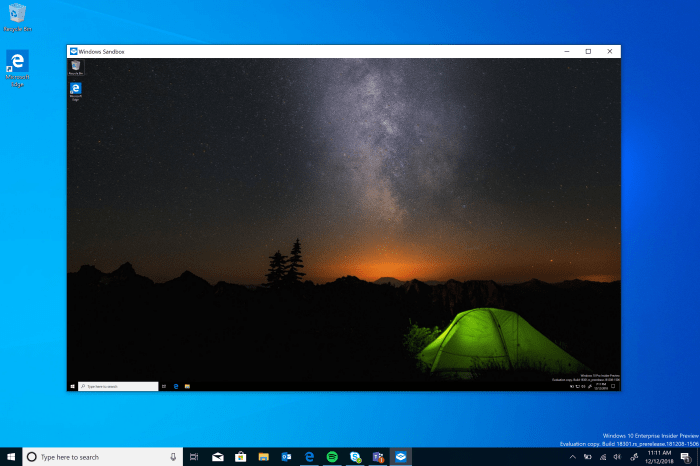
What’re the Advantages of Windows Sandbox?
There are several reasons why you might want to run an app in a sandboxed environment. Maybe you’ve received an app as an attachment or you’re downloading something and you’re just not sure it’s safe. Instead of taking a risk or going through the steps of setting up a virtual machine, running apps in Windows Sandbox will give you extra peace of mind knowing you can test the program out first without compromising your main system.
We will be taking a close look at using Windows Sandbox as Microsoft gets closer to rolling out the next feature update. But for more technical details on how Windows Sandbox runs under the hood, check out Hari Pulapaka’s post on the Microsoft Community blog. You’ll find that the isolated environment is light on system resources and only uses around 100 MB of disk space. No VHD is or separate Windows license is required. Each time it runs, it’s a brand-new clean installation on Windows 10 – which is good for developers who need to test their apps during the dev cycle.
How to Enable the New Windows 10 Sandbox Feature to Safely Test Apps
ByBrian Burgess
Last Updated on December 21, 2018

Windows Sandbox in Windows 10 allows you to safely run untrusted apps in an isolated virtual environment and keep your main system safe from malware.
COMMENTS
When Microsoft rolled out Windows 10 build 18305 to Insiders in the Fast ring, it also madeWindows Sandbox available. The sandbox feature allows you to run sketchy or untrusted applications in an isolated environment that doesn’t affect the rest of your system. Typically, you could do this by setting up a virtual machine – which takes time and system resources. But Microsoft is making the process easier by implementing Windows Sandbox in the upcoming feature update. Here is a look at how to enable and use the new feature.
Note: This is only available for Pro and Enterprise versions of Windows 10 (build 18305 or higher). Your system will also need to meet the following requirements:
- x64 architecture
- Virtualization capabilities enabled in BIOS
- At least 4GB of RAM (8GB recommended)
- At least 1 GB of free disk space (SSD recommended)
- At least 2 CPU cores (4 cores with hyperthreading recommended)
To enable Windows Sandbox, hit the Windows key and type: turn windows features on or off and choose the top result or hit Enter.

The Windows Features window where you can turn different features on or off will open. Scroll down the list and check the “Windows Sandbox” option and click OK. Then simply follow the on-screen wizard to finish installing it – a restart will be required.

Once installed, you can simply run Windows Sandbox from the Start menu with elevated privileges. Copy the executable file you want to run to the Windows Sandbox and run it like you normally would.

What’re the Advantages of Windows Sandbox?
There are several reasons why you might want to run an app in a sandboxed environment. Maybe you’ve received an app as an attachment or you’re downloading something and you’re just not sure it’s safe. Instead of taking a risk or going through the steps of setting up a virtual machine, running apps in Windows Sandbox will give you extra peace of mind knowing you can test the program out first without compromising your main system.
We will be taking a close look at using Windows Sandbox as Microsoft gets closer to rolling out the next feature update. But for more technical details on how Windows Sandbox runs under the hood, check out Hari Pulapaka’s post on the Microsoft Community blog. You’ll find that the isolated environment is light on system resources and only uses around 100 MB of disk space. No VHD is or separate Windows license is required. Each time it runs, it’s a brand-new clean installation on Windows 10 – which is good for developers who need to test their apps during the dev cycle.



